What is an STP
A signal transfer point (STP), is a router for telephone traffic within the SS7 network. An STPs primary task is to determine the best path for two signaling end points (SEPs) to communicate. As such, STPs form the backbone of the SS7 network. Attached to this backbone are the Service Switching Points (SSPs) and Service Control Points (SCPs). Each SSP and SCP is assigned a "home pair" of STPs that it is directly connected to. An SCP database containing lookup information to facilitate call routing might be connected to an SSP although an SCP is more typically connected to an STP.
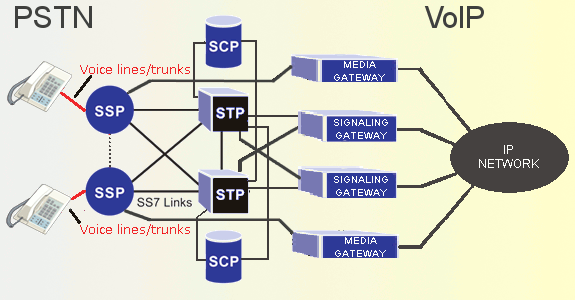
STPs at the heart of a mesh network routing traffic to and from SSPs, other STPs and gateway equipment to the IP network. As shown by the dashed line, SSPs can sometimes have direct links to one another such as for high traffic volume in metropolitan areas, or when an STP is not available such as commonly occurs in Europe.
SS7 and VoIP
In a modern network where the public switched telephone network interfaces with IP networks, an STP in addition to communicating with other STPs and SSPs, also communicates with gateways to the IP network. In such a modern network, the service end points (SEPs) for an STP are SSPs, STPs and gateway devices to the IP network.
Most messages are not originated by an STP, they are merely passed along. When an STP does originate messages, they are related to network management and global title translation (SS7 equivalent to IP routing). STPs also provide firewall functionality. STPs are paired for redundancy and are located geographically apart in order to not expose both to the same hazards.
An STP is one type of SS7 network node or signaling point (SP). An SCP and SSP are also service points. SSPs create packets (signal units), send those messages to other SSPs and send queries to remote shared databases to find out how to route calls. SSPs are the central office switches that originate, terminate or tandem (through connect) calls.
STPs (like all SPs) are addressed by a unique point code and are connected to each other by signaling links. Up to 16 links may be used between STPs and any other SP. Links are logically grouped into a linkset. Depending on where they are in the network, links may be termed A through F links. An STP may operate at three network levels; national STP, international STP and as a gateway STP.




